Optic Lens Developed for NSLS-II Beamline Achieves 11-nm Focus
February 21, 2014
At the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), now under construction at Brookhaven National Laboratory, the Hard X-ray Nanoprobe beamline (HXN) will enable scientists to image structures at ever-smaller spatial scales. HXN’s long-range goal is to achieve a resolution of 1 nanometer (nm), or a billionth of a meter, completely eliminating the long-standing resolution gap between x-ray and electron microscopes. Hard x-rays exhibit excellent structural, elemental and chemical sensitivity and are particularly suited for in-situ studies that are challenging for electrons.
Image showing propagation of reconstructed wavefront, revealing the focusing performance of multilayer Laue lens developed for HXN Beamline at NSLS-II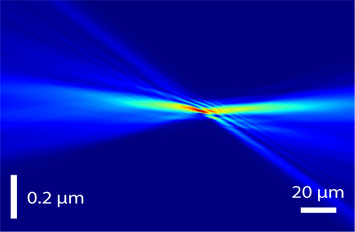 enlarge
enlarge
Brookhaven scientists, in collaboration with researchers from other institutions, have successfully focused 12 keV x-rays down to 11 nm using a novel x-ray optic called multilayer Laue lens (MLL). They published their results in Nature’s Scientific Reports, December 2013.
The team was able to analyze their MLL’s focusing performance to unprecedented details using a technique known as ptychography. “With ptychography, we can visualize how the x-rays are traveling from the lens to the focus and to an arbitrary point in the optical path. Therefore, we do not have to use conventional knife-edge scans to quantify lens aberrations,” said Xiaojing Huang, the paper’s first author. The ptychography analysis quantified the lens aberrations at a 0.3 wave period, very close to a quarter wave period. This represents a rigorous threshold value for “diffraction-limited” focusing.
The Brookhaven-fabricated MLL has a 43-micron aperture – the largest reported MLL size. It accepts substantially more x-rays than earlier MLLs and offers a significantly larger working distance, needed for in-situ experiments. It also contains an astonishing total of 6,510 layers, with thicknesses ranging from 4 to 21 nm.
Explained Nathalie Bouet, who is in charge of the MLL fabrication for NSLS-II, “The overall thickness accuracy for this MLL is insanely high – better than the size ratio of a penny to the height of the Empire State Building!”
“This is an important step toward our ultimate goal of achieving 1 nm,” added coauthor Hanfei Yan.
Yong Chu, the paper’s corresponding author and HXN group leader, stressed, “The HXN beamline is a highly complex instrument requiring expertise in many different areas. It is important to acknowledge the team effort by the committed collaborators at NSLS-II and at Argonne Lab’s Advanced Photon Source.” He also noted that the demonstrated MLL performance gives confidence to the team that HXN will deliver x-ray microscopy capabilities with an initial resolution of 10 nm, “encouraging news for the scientific community anticipating its completion.”
The paper is coauthored by Xiaojing Huang, Hanfei Yan, Evgeny Nazaretski, Raymond Conley, Nathalie Bouet, Juan Zhou, Kenneth Lauer, Li Li, Daejin Eom, Daniel Legnini, Ross Harder, Ian K. Robinson and Yong S. Chu. Their work was supported by the Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation.
2014-4676 | INT/EXT | Newsroom