Structure and Function of Fusicoccadiene Synthase, a Hexameric Bifunctional Diterpene Synthase
November 17, 2016
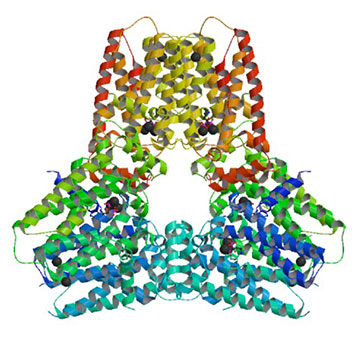
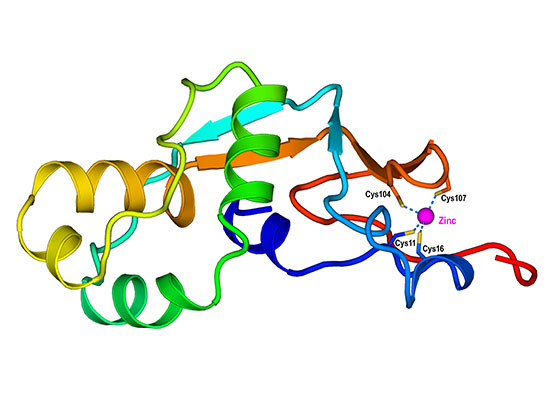
The Christianson Group (University of Pennsylvania, Chemistry Department) recently reported the structure and function of Fusicoccin Synthase ((2016) ACS Chem.Biol. DOI 10.1021/acschembio.5b00960). Generated by the fungal pathogen Phomopsis amygdali that causes the plant disease constriction canker, first discovered in New Jersey peach farms in 1930, Fusicoccin A a diterpene glucoside phytotoxin is emerging as a new lead in cancer chemotherapy. To understand the function and the pathway the Christianson group used x-ray crystallography, solving various molecular structures, from data collected at the NSLS, X29, APS, 24ID and SSRL 14-1 (supported by NSLS staff) in combination with other methods; small-angle X-ray scattering data yielded well-defined molecular envelopes illustrating plausible models for hexamer assembly. This was further confirmed by Gel filtration chromatography and analytical ultracentrifugation experiments indicating that full-length fusicoccadiene synthase adopts hexameric quaternary structure.
2016-6733 | INT/EXT | Newsroom