CERN Experiment Traps Antimatter Atoms for 1,000 Seconds
June 6, 2011
The following news release, which is being distributed by CERN, the European laboratory for particle physics, describes how an international team of researchers working at CERN trapped and stored atoms of antimatter for longer than 16 minutes. The main component of the antimatter trap is an octupole (eight-magnetic-pole) magnet that was fabricated at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory in 2006. Using a specially developed 3D winding machine, the Brookhaven team built the magnet directly onto the outside of the trap. For more information about Brookhaven’s role, contact Kendra Snyder, ksnyder@bnl.gov, 631-344-8191, or Peter Genzer, genzer@bnl.gov, 631-344-3174.
 enlarge
enlarge
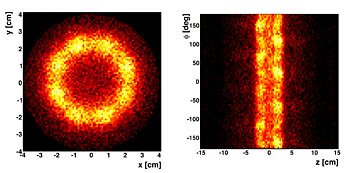
Untrapped antihydrogen atoms annihilating on the inner surface of the ALPHA trap. These are measured by the ALPHA annihilation detector. The events are concentrated at the electrode radius of about 22.3 mm. The coordinates are defined in the Nature article, Figure 1b.
Geneva — In a paper published online by the journal Nature Physics today, the ALPHA experiment at CERN reports that it has succeeded in trapping antimatter atoms for over 16 minutes: long enough to begin to study their properties in detail. ALPHA is part of a broad program at CERN’s antiproton decelerator (AD) investigating the mysteries of one of nature’s most elusive substances.
Today, we live in a universe apparently made entirely of matter, yet at the big bang matter and antimatter would have existed in equal quantities. Nature seems to have a slight preference for matter, which allows our universe and everything in it to exist. One way of investigating nature’s preference for matter is to compare hydrogen atoms with their antimatter counterparts, and that’s what makes today’s result important.
“We can keep the antihydrogen atoms trapped for 1,000 seconds,” explained ALPHA spokesperson Jeffrey Hangst of Aarhus University. “This is long enough to begin to study them — even with the small number that we can catch so far.”
In the paper published today, some 300 trapped antiatoms are reported to have been studied. The trapping of antiatoms will allow antihydrogen to be mapped precisely using laser or microwave spectroscopy so that it can be compared to the hydrogen atom, which is among the best-known systems in physics. Any difference should become apparent under careful scrutiny. Trapping antiatoms could also provide a complementary approach to measuring the influence of gravity on antimatter, which will soon be investigated with antihydrogen by the AEgIS experiment.
Another important consequence of trapping antihydrogen for long periods is that the antiatoms have time to relax into their ground state, which will allow ALPHA to conduct the precision measurements necessary to investigate a symmetry known as CPT. Symmetries in physics describe how processes look under certain transformations. C, for example, involves swapping the electric charges of the particles involved in the process. P is like looking in the mirror, while T involves reversing the arrow of time.
Individually, each of these symmetries is broken — processes do not always look the same. CPT, however, says that a particle moving forward through time in our universe should be indistinguishable from an antiparticle moving backwards through time in a mirror universe, and it is thought to be perfectly respected by nature. CPT symmetry requires that hydrogen and antihydrogen have identical spectra.
“Any hint of CPT symmetry breaking would require a serious rethink of our understanding of nature,” said Hangst. “But half of the universe has gone missing, so some kind of rethink is apparently on the agenda.”
The next step for ALPHA is to start performing measurements on trapped antihydrogen, and this is due to get underway later this year. The first step is to illuminate the trapped anti-atoms with microwaves, to determine if they absorb exactly the same frequencies (or energies) as their matter cousins.
“If you hit the trapped antihydrogen atoms with just the right microwave frequency, they will escape from the trap, and we can detect the annihilation — even for just a single atom,” explained Hangst. “This would provide the first ever look inside the structure of antihydrogen — element number 1 on the anti-periodic table.”
Contact
CERN Press Office
press.office@cern.ch
+41 22 767 34 32
+41 22 767 21 41
2011-11289 | INT/EXT | Newsroom