Study Sheds Light on Photosynthesis in Iron-Low Leaves
The Guerinot Lab uses genetics to study a critical mineral deficiency in plants
October 27, 2021
 enlarge
enlarge
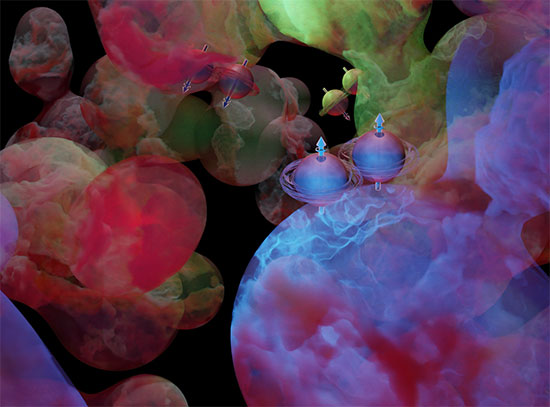
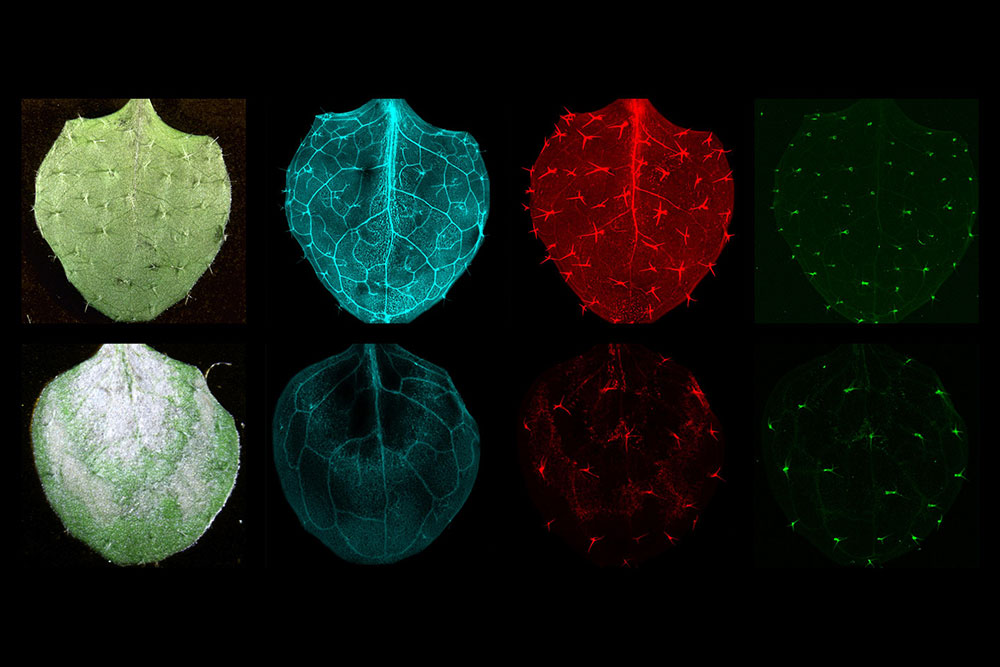
Top, a normal leaf's nutrient distribution. Bottom, distribution in a light-bleached mutant leaf. Synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry image by Nabila Riaz.
The following news release, originally issued by Dartmouth University, describes a paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. The paper details how a team of researchers studied the influence of iron-deficiency on photosynthesis in plants. They found how iron-deficient plants optimize photosynthesis to protect themselves from absorbing too much light. To understand the distribution of important metals (calcium, iron, and potassium) within the iron-deficient plants, the research team used x-ray fluorescence microscopy at the X-ray Fluorescence Microprobe (XFM) beamline at the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility located at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory. For more information on Brookhaven’s role in this research, contact Cara Laasch, 631-344-8458, laasch@bnl.gov.
Researchers have identified how iron-deficient plants optimize photosynthesis to protect themselves from absorbing too much light, according to a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research comes as the globe considers the effects of climate change on how food is grown.
“This study adds to what we know about how plants respond to environmental change at a critical time for our human food supply,” says Mary Lou Guerinot, professor of biological sciences and senior researcher of the study.
Iron is central to photosynthesis, the process that converts light energy into chemical energy in plants. Since people obtain a majority of their calories and nutrients from plants, it is important that researchers understand how plants process the mineral.
The research focuses on activity in chloroplasts, where 90% of the iron in plant leaves is stored and where photosynthesis takes place.
 enlarge
enlarge
Mary Lou Guerinot, left, professor of biological sciences, and Nabila Riaz, Guarini '22. (Photo by Eli Burakian '00)
“Many strategies to optimize iron usage have been documented, but we knew fairly little about the mechanisms of how chloroplasts adapt to iron deficiency prior to this study,” says Garo Akmakjian, Guarini ’18, lead author of the paper and now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California, Riverside.
The research team, which included Nabila Riaz, Guarini ’22, followed the cause of light-induced leaf bleaching observed in an iron-deficient plant. They identified two regulatory proteins that protect plants from absorbing too much light during iron deficiency.
Technical images taken by Riaz demonstrate the way iron and other nutrients react to the absence of the regulatory proteins.
“Being able to use advanced technology to image where nutrients are localized in living plant tissues is exciting and increases our understanding of how elements distribute themselves in response to environmental changes,” says Riaz.
The iron uptake system in plants is regulated by a cascade of activities, many of which have been discovered by Dartmouth’s Guerinot Lab.
The team hopes that understanding how plants adapt their photosynthetic machinery during iron deficiency may allow researchers to optimize plant growth in soils where iron is not naturally available.
“With climate change, where and how we grow crops is changing,” says Guerinot. “In the future, we won’t have the luxury of only growing crops in fertile soils rich in nutrients and with plenty of water.”
2021-19226 | INT/EXT | Newsroom