Technologies Available for License
Categories: advanced materialselectronics & instrumentation
2014-025: Slits for depth resolution using X-ray diffraction
Invention: 2014-025
Patent Status: U.S. Patent Number 9,875,821 was issued on January 23, 2018
For technical and licensing related questions, email tcp@bnl.gov.
Summary
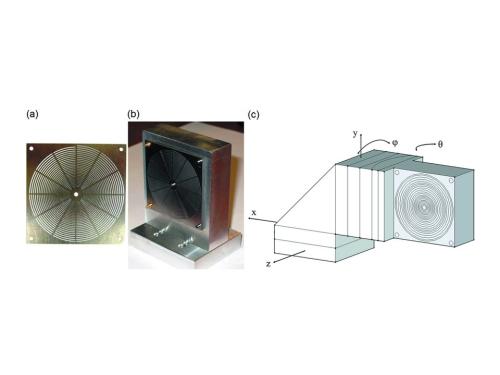
(a) A completed laser-cut spiderweb slit plate. (b) Sixteen plates are mounted on an aluminium holder and aligned with dowel pins. (c) The holder is mounted onto three translation stages, a rotation stage and a mini goniometer, in order to properly align into the diffracted X-rays.
Understanding the three dimensional structure of materials and their in situ response to processes is of great interest to material scientists. X-ray powder diffraction studies allow scientists to non-destructively analyze complex material mixtures. Currently, conical slits are being used in X-ray diffraction mapping to study few predefined gauge volumes. The spiderweb slit technology described here allows for any diffraction from the defined gauge volume to be measured by the detector, thereby allowing one to study different materials in layered samples.
Description
The spiderweb slit function by matching the geometry of Debye-Scherrer diffraction cones from powder or polycrystalline materials. The diffracted x-rays originating from the gauge volume of sample pass through a set of slits and are recorded by the detector, while diffracted rays outside the gauge volume are absorbed by the walls defining the slits.
Benefits
The use of the slit allows one to: 1. Reduce background diffraction from sample containers. This will allow one to study samples within a container. 2. Analyze materials that are present in different layers.
Applications and Industries
The slits can be used in lab top X-Ray Diffractometers for the study of complex layered materials in-situ.
Journal Publication & Intellectual Property
- US 9,875,821 B2 (.pdf)
- US 10,395,789 B2 (.pdf)
- Fabrication and testing of a newly designed slit system for depth-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements (.pdf)
Tags: in-situ
Contacts
-

Poornima Upadhya
Manager Technology Transfer & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-4711, pupadhya@bnl.gov
-

Avijit Sen
IP Licensing & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-3752, asen@bnl.gov




