- Home
-
Research Groups
Division Groups
- Artificial Photosynthesis
- Catalysis: Reactivity & Structure
- Electrochemical Energy Storage
- Electron- and Photo-Induced Processes for Molecular Energy Conversion
- Neutrino and Nuclear Chemistry
- Surface Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis
Associated Groups
- Catalysis for Alternative Fuels Production
- Nanostructured Interfaces for Catalysis
- Structure and Dynamics of Applied Nanomaterials
- People
- Operations
- News
- Events
Artificial Photosynthesis
Effects of a Proximal Base on Water Oxidation and Proton Reduction Catalyzed by Geometric Isomers of [Ru(tpy)(pynap)(OH2)]2+
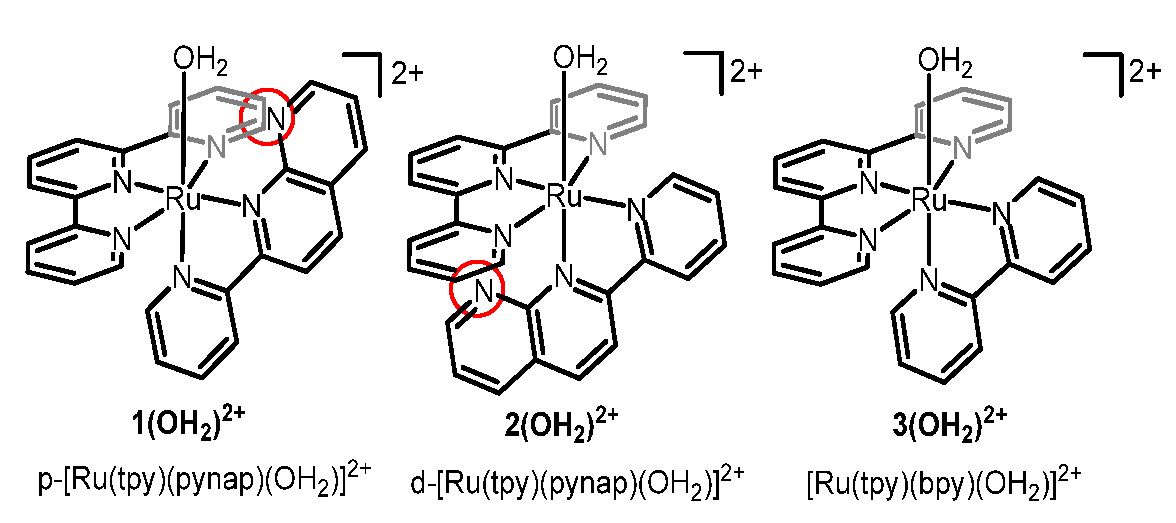 The
importance of pendent bases in promoting proton-coupled electron-transfer
(PCET) reactions with low activation barriers has been discussed for H+
reduction or H2 oxidation in MeCN by many groups. PCET is also
essential for the 4e– oxidation of water in order to mitigate charge buildup
and to reduce overpotential. We investigated the redox and spectroscopic
properties, and report the intriguing catalytic activity for the oxidation
of H2O and the reduction of protons with geometric isomers of Ru
complexes with pendent bases. While 1(OH2)2+
shows catalytic activity toward proton reduction, but not toward water
oxidation, the geometric isomer, 2(OH2)2+,
exhibits the opposite behavior.
The
importance of pendent bases in promoting proton-coupled electron-transfer
(PCET) reactions with low activation barriers has been discussed for H+
reduction or H2 oxidation in MeCN by many groups. PCET is also
essential for the 4e– oxidation of water in order to mitigate charge buildup
and to reduce overpotential. We investigated the redox and spectroscopic
properties, and report the intriguing catalytic activity for the oxidation
of H2O and the reduction of protons with geometric isomers of Ru
complexes with pendent bases. While 1(OH2)2+
shows catalytic activity toward proton reduction, but not toward water
oxidation, the geometric isomer, 2(OH2)2+,
exhibits the opposite behavior.




