- Home
-
Research Groups
Division Groups
- Artificial Photosynthesis
- Catalysis: Reactivity & Structure
- Electrochemical Energy Storage
- Electron- and Photo-Induced Processes for Molecular Energy Conversion
- Neutrino and Nuclear Chemistry
- Surface Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis
Associated Groups
- Catalysis for Alternative Fuels Production
- Nanostructured Interfaces for Catalysis
- Structure and Dynamics of Applied Nanomaterials
- People
- Operations
- News
- Events
Structure and Dynamics of Applied Nanomaterials
Application of operando XAS, XRD and Raman Spectroscopy for phase speciation in WGS reaction catalysts
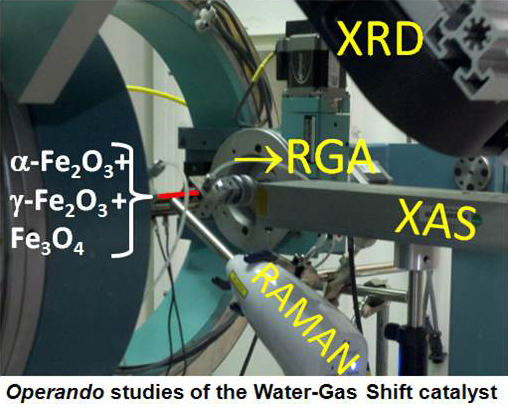 The structural and compositional changes of the partially reduced iron oxide Fe2O3 and 3% chromium oxide-modified iron oxide (3% Cr2O3 / Fe2O3) catalysts before, during and after the water gas shift (WGS) reaction are reported. The measurements were performed by collecting X-ray Absorption Fine structure, X-ray Diffraction and Raman spectroscopy data on the catalysts, and the mass spectrometry data of reactants and products, all done in a single experiment. These materials demonstrated marked structural disorder and compositional heterogeneity that are peaked in their catalytically active states. The main findings revealed in the result of combining multiple techniques include: the role of Cr in stabilizing the low temperature γ-Fe2O3 phase, the nature of the disordered phase in the active state of the catalysts and the possible deactivation mechanism.
The structural and compositional changes of the partially reduced iron oxide Fe2O3 and 3% chromium oxide-modified iron oxide (3% Cr2O3 / Fe2O3) catalysts before, during and after the water gas shift (WGS) reaction are reported. The measurements were performed by collecting X-ray Absorption Fine structure, X-ray Diffraction and Raman spectroscopy data on the catalysts, and the mass spectrometry data of reactants and products, all done in a single experiment. These materials demonstrated marked structural disorder and compositional heterogeneity that are peaked in their catalytically active states. The main findings revealed in the result of combining multiple techniques include: the role of Cr in stabilizing the low temperature γ-Fe2O3 phase, the nature of the disordered phase in the active state of the catalysts and the possible deactivation mechanism.
A. Patlolla, E. V. Carino, S. Ehrlich, E. Stavitski, A. I. Frenkel
Application of operando XAS, XRD and Raman Spectroscopy for phase speciation in water gas shift reaction catalysts
Invited article, ACS Catalysis 2, 2216-2223 (2012)




