MIT/National Labs Team Visualizes Complex Electronic State
Multidisciplinary group solves mystery of how a potential battery electrode material behaves
May 21, 2014
By David L. Chandler | MIT News Office
 enlarge
enlarge
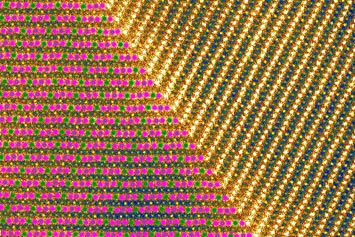
The internal molecular structure of the electrode compound reveals what the researchers call the "superstructure." At right is a scanning transmission electron microscope image of the material, and, at left, the image is color-coded based on electrical properties: Each green dot stands for a stripe of manganese plus-4 ions; purple dots, for manganese plus-3 ions; and mixed color dots (green inside purple), for stripes with both ions.
The following news release was first issued by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory made crucial contributions to the research. Scientist Dong Su of the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) took scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) measurements of the samples and helped analyze the data, directly revealing the collective ordering and unexpected distortion of electrochemically inserted sodium. Physicists Jianming Bai of Photon Sciences and Feng Wang of Sustainable Energy Technologies performed x-ray diffraction experiments at the National Synchrotron Light Source (NSLS) that confirmed the results.
A material called sodium manganese dioxide has shown promise for use in electrodes in rechargeable batteries. Now a team of researchers has produced the first detailed visualization—down to the level of individual atoms—of exactly how the material behaves during charging and discharging, in the process elucidating an exotic molecular state that may help in understanding superconductivity.
The new findings are reported this week in the journal Nature Materials, in a paper by MIT postdoc Xin Li, professors Young Lee and Gerbrand Ceder, also of MIT, and 12 others.
The phenomenon the team investigated—known as the cooperative Jahn-Teller effect—“is a basic piece of physics that has been well-known historically,” explains Ceder, the R.P. Simmons Professor of Materials Science and Engineering. It describes how the positions of atoms in certain compounds can be slightly distorted, changing the material’s electrical and magnetic properties.
"We began the electron microscopy work with MIT fellows about two years ago and combined our results with theoretical calculations to figure out the structure of NMO—it’s taken this long to run calculations and confirm those results with x-ray and neutron scattering so fantastically. Now, we’re finally ready for our findings to impact energy research and technology.”
— CFN Scientist Dong Su
“It is associated with a lot of interesting phenomena,” Ceder says—so a better understanding could be useful both in advancing our knowledge of physics and in potential applications, from improved batteries to new kinds of electronics.
While the Jahn-Teller phenomenon is well known, Ceder says it’s a bit unusual to see it in battery compounds such as the sodium manganese dioxide now under investigation as a possible lower-cost substitute for the lithium-based electrodes in lithium-ion batteries.
Such rechargeable batteries work when an electrical current pulls ions out of an electrode during charging, then returns them to the electrode as the battery is used. The arrangement of atoms within the material “is very ordered, and normally the ordering is driven by fairly standard physics,” Ceder says. “But in this material, the order is completely driven by the Jahn-Teller effect.”
Understanding how that difference affects charging and discharging could be important in guiding teams around the world who are seeking to improve the performance of such batteries, but it proved a daunting challenge for the MIT team.
The team combined density functional theory with technologies including electron diffraction; synchrotron X-ray diffraction; neutron diffraction; and aberration-corrected atomic-resolution scanning microscopy for direct visualization. Using these methods, the researchers showed that the material produces a “superstructure” governed by the Jahn-Teller effect; at very low temperatures, it produces a kind of “magnetic stripe sandwich,” with alternating stripes of ferrimagnetic and antiferromagnetic atomic chains.
“This is fundamental work,” Li says, to determine “any intrinsic capacity limits to sodium manganese dioxide” — such as how much charge it can hold, or how many times it can go through the charge-discharge cycle without degradation. The ultimate goal is to find out “how [to] make a higher-capacity sodium-ion battery electrode,” Li says.
In addition to possible battery applications, the work led to the finding that sodium manganese dioxide forms bands of magnetic domains at temperatures of 60 kelvins (-352 degrees Fahrenheit) or less. This finding, Li says, may be important to the emerging field of spin electronics, where the spin states of electrons, rather than their electrical charges, carry and store information.
Even before this new research, Li says, batteries made of this sodium-ion composition “showed comparable capacity to the commercial lithium-ion batteries,” which are one of the leading technologies in production today. While no companies are now producing sodium-ion batteries, the technology has great potential: Sodium is more abundant, less expensive, and safer to work with than lithium.
“This is still fairly basic research,” Li says, adding: “Understanding always pushes us forward, especially in this field. You only make progress by understanding these materials better.”
The work also included researchers Dong Su at Brookhaven National Laboratory, Juan-Carlos Idrobo at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and Jeffrey W. Lynn at the National Institute of Standards and Technology, as well as seven others from MIT. It was partly funded by the Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology and the U.S. Department of Energy.
2014-4905 | INT/EXT | Newsroom