Technologies Available for License
Category: electronics & instrumentation
2013-035: Circuits for Current-Output Peak Detection
Invention: 2013-035
Patent Status: U.S. Patent Number 9,551,734 was issued on January 24, 2017
For technical and licensing related questions, email tcp@bnl.gov.
Summary
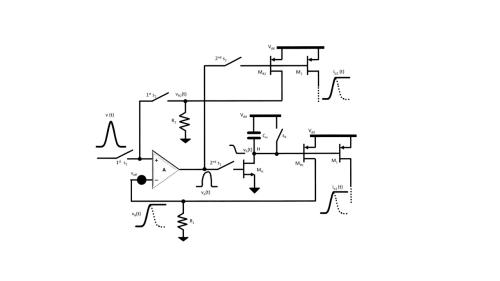
Schematic diagram of a current-output peak detector circuit.
There is a need to develop a peak detector that offers high degree of precision peak detection and capable of operating with rail-to-rail voltage inputs and providing an output current for operation with current-input processing electronics. This invention describes a current-output peak detector circuit that works in two phases. The peak detector circuit includes switches to switch the peak detector circuit from the first phase to the second phase upon detection of the peak voltage of an input voltage signal. The peak detector generates a current output with a high degree of accuracy in the second phase.
Description
A peak detector circuit generating a current output, includes an amplifier, a negative input terminal, and an output terminal. The positive input terminal of the amplifier is attached with an input voltage signal through a first switch, the negative input terminal is attached with a first resistor, the output terminal is attached with the gate of a hold transistor MH through a second switch, and the drain of the hold transistor is coupled with a first terminal of a hold capacitor. The peak detector circuit further includes a first transistor MR1. The gate of the first transistor MR1 is attached with the drain of the hold transistor and the gate of a second transistor, the drain of the first transistor MR1 is attached with the negative input terminal of the amplifier, and the second transistor is composed of n1 copies of the first transistor MR1 connected in parallel and n1 is an integer. The sources of the first and second transistors and the second terminal of the hold capacitor are attached to a supply voltage.
Benefits
The peak detector operates with rail-to-rail input voltages but without being affected by non-linear errors due to voltage offsets at the complementary differential input stages.
Applications and Industries
The potential application of this technology includes developing devices for high-resolution measurements (e.g., radiation detection).
Journal Publication & Intellectual Property
- US 9,551,734 B2 (.pdf)
Contacts
-

Poornima Upadhya
Manager Technology Transfer & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-4711, pupadhya@bnl.gov
-

Avijit Sen
IP Licensing & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-3752, asen@bnl.gov




