- Home
-
Research Groups
Division Groups
- Artificial Photosynthesis
- Catalysis: Reactivity & Structure
- Electrochemical Energy Storage
- Electron- and Photo-Induced Processes for Molecular Energy Conversion
- Neutrino and Nuclear Chemistry
- Surface Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis
Associated Groups
- Catalysis for Alternative Fuels Production
- Nanostructured Interfaces for Catalysis
- Structure and Dynamics of Applied Nanomaterials
- People
- Operations
- News
- Events
Structure and Dynamics of Applied Nanomaterials
Intracluster atomic and electronic structural heterogeneities in supported nanoscale metal catalysts
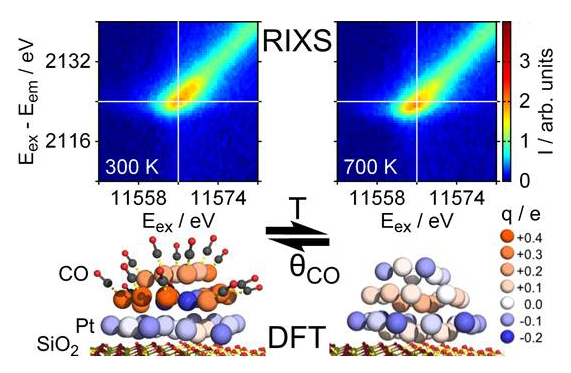 This work reveals and quantifies the inherent intracluster heterogeneity in the atomic structure and charge distribution present in supported metal catalysts. The results demonstrate that these distributions are pronounced and strongly coupled to both structural and dynamic perturbations. They also serve to clarify the nature of the dynamic bonding of nanoscale catalytic metal clusters with their supports, and the mediation of these properties due to the presence of adsorbates. These findings are supported by theoretical modeling and experimental data measured for an exemplary supported metal catalyst, Pt supported on silica, using: in-situ high energy resolution X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopies; in-situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy; and ex-situ scanning transmission electron microscopy.
This work reveals and quantifies the inherent intracluster heterogeneity in the atomic structure and charge distribution present in supported metal catalysts. The results demonstrate that these distributions are pronounced and strongly coupled to both structural and dynamic perturbations. They also serve to clarify the nature of the dynamic bonding of nanoscale catalytic metal clusters with their supports, and the mediation of these properties due to the presence of adsorbates. These findings are supported by theoretical modeling and experimental data measured for an exemplary supported metal catalyst, Pt supported on silica, using: in-situ high energy resolution X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopies; in-situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy; and ex-situ scanning transmission electron microscopy.
A. Elsen, U. Jung, F. D. Vila, Y. Li, O. V. Safonova, R. Thomas, M. Tromp, J. J. Rehr, R. G. Nuzzo, A. I. Frenkel
Intracluster atomic and electronic structural heterogeneities in supported nanoscale metal catalysts
J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 25615-25627 (2015)




