Technologies Available for License
Category: electronics & instrumentation
2021-009: EDWARD - Event Driven with Access and Reset Decoder readout architecture with non-priority arbitration for multichannel data sources
Invention: 2021-009
Patent Status: U.S. Patent Number 125,178,552 was issued on January 6, 2026
For technical and licensing related questions, email tcp@bnl.gov.
Summary
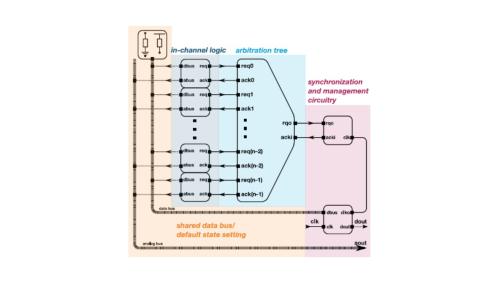
Scheme: Block-level diagram of the readout management system.
Data readout or computer network systems that either collect or transmit data starve for optimal usage of the available bandwidth of the links. There is a need to build systems that can make collecting data from spatially distributed sources such as distributed grid of in-a-field deployed sensors, computers on a network or cells in content addressable memories, processing channels in neuromorphic chips, or elements in 1D (strip) or 2D (pixelated) radiation detectors more efficient and economical. This Brookhaven invention, EDWARD, describes the protocol, architecture and features for a readout ASIC that can acquire data from multiple sources, operating asynchronously such that the order of channels to transmit concurrently is independent of the position of the data source.
Description
EDWARD, the new event driven data readout system (scheme) is adapted for the efficient transmission of data from multiple data sources. The data sources can be one-dimensional structures, two-dimensional structures, and/or any other form. EDWARD is event-driven i.e., no synchronization is needed for asynchronous input data. EDWARD not only allows sending additional data, beyond the active channel but also allows sending analog data together with digital ones. It provides a reliable mechanism that prevents the collision of channels accessing a common data bus. No channel starves for allocation of time slots for sending their data off, i.e. there is no situation when an access to the readout resources is unfairly or perpetually denied to some of the channels. The mechanism is based on arbitration tree build as a binary tree using arbitration cell that have mutually exclusive outputs. The EDWARD architecture is an alternative for the commonly used token-passing scheme and does not carry-on deficiencies of the widely used Token Passing Architecture such as the deterministic order of the read-out channels and a varied delay in accessing the channels as a function of their location at the beginning or at the end of the token passing route.
Benefits
With the event-driven design and the use of an arbitration tree in the EDWARD system, synchronization with external systems is done at the global logic level, so there is no need to distribute the clock signal directly to the channels. This approach saves area, power, and system complexity because no clock tree is required to be implemented. The flexibility of the EDWARD architecture allows it to be used in a wide variety of applications where asynchronous data is acquired from spatially distributed sources. Additionally, this flexibility allows dynamic configuration based on the actual needs during the data collection.
Applications and Industries
Integrated readout of strip and pixel radiation detectors as well as building neuromorphic or other event-driven processing circuits.
Journal Publication & Intellectual Property
- Event driven readout architecture with non-priority arbitration for radiation detectors (.pdf)
- WO 2022/221068 A1 (.pdf)
- Investigation of Timing Properties for an Event Driven with Access and Reset Decoder Readout Architecture for a Pixel Array (.pdf)
- Integration of EDWARD readout architecture in full-field fluorescence imaging detector (.pdf)
- US 12,517,855 B2 (.pdf)
Contacts
-

Poornima Upadhya
Manager Technology Transfer & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-4711, pupadhya@bnl.gov
-

Avijit Sen
IP Licensing & Commercialization
Technology Commercialization
(631) 344-3752, asen@bnl.gov




