Studying "Excitons" in a Novel Magnetic Material
Understanding these quasiparticles could be key to unlocking and harnessing new technologies
August 19, 2024
 enlarge
enlarge
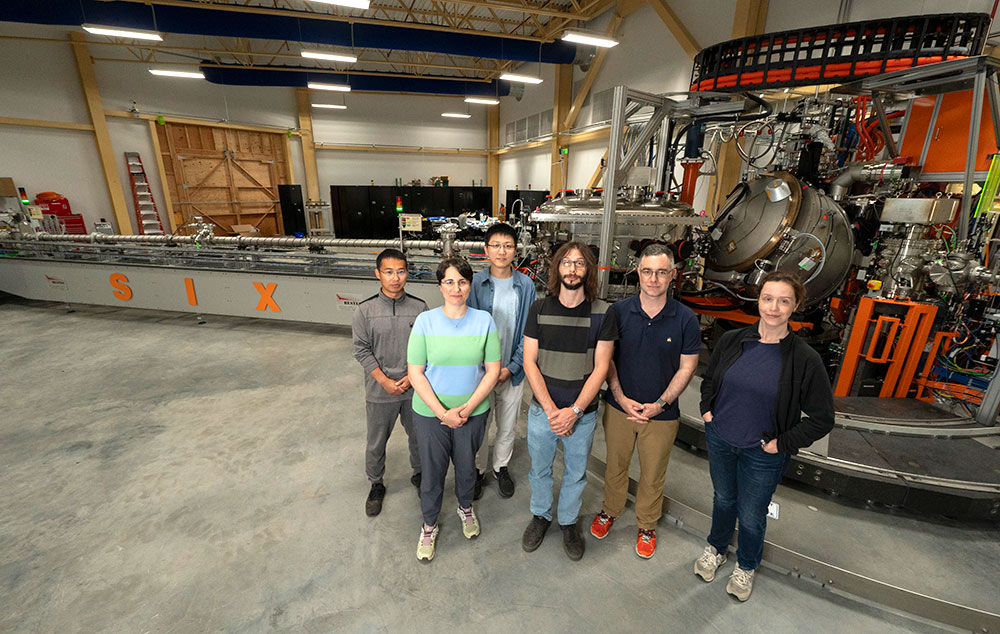
From left, the paper's authors Jiemin Li, Valentina Bisogni, Wei He, Jonathan Pelliciari, Mark Dean, and Jennifer Sears at the Soft Inelastic X-ray Scattering (SIX) beamline of the National Synchrotron Light Source II facility at Brookhaven National Laboratory. (Jessica Rotkiewicz/Brookhaven National Laboratory)
A research group led by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has uncovered details about the formation and behavior of mobile, microscopic, particle-like objects called “excitons” in a class of materials known as van der Waals magnets. Their work helps establish a picture of the complex relationship between the optical and magnetic properties of these materials, which display intriguing characteristics that could one day lead to brand-new technologies based on magnetism, such as information storage.
The study is described in a paper in the April 25, 2024, online edition of the journal Nature Communications.
The researchers studied the crystalline material, nickel phosphorus trisulfide (NiPS3), using the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a DOE Office of Science user facility located at Brookhaven. NSLS-II produces intense beams of X-ray light that are used to study a wide range of materials and biological samples, from battery compounds to proteins.
An exciton consists of an electron and a “hole” — a space in a crystal that lacks an electron and behaves as a positively charged particle — that are coupled together and move as a unit. Discovering excitons in NiPS3 has sparked significant interest in this particular van der Waals material. This is due to the possible strong link between the excitons and the underlying magnetic structure, suggesting a route to understanding, and perhaps even controlling, excitons via magnetism. But despite several studies, scientists have been so far unable to uncover the exciton structure and motion in NiPS3.
The group tackled this challenge using an X-ray technique known as resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS), available at NSLS-II's Soft Inelastic X-ray Scattering (SIX) beamline. This cutting-edge experimental station was designed to use NSLS-II's ultrabright X-ray beams to study the electronic properties of solid materials, revealing energy behaviors at a very high resolution.
“What is the fundamental nature of an exciton? How does it interact with magnetism? These are two of the questions we looked to RIXS to help us answer,” said Brookhaven physicist Mark Dean, one of the paper’s authors.
In RIXS, the X-ray photons hit the electrons in the material and scatter off in many directions. At SIX, scientists can “catch” these photons and measure their momenta and energies with extremely high resolution. With this information, using software developed at Brookhaven, they can work backward to study the properties of the electrons and holes in the material.
They found that exciton formation and propagation through the NiPS3 crystal is governed by a physics principle called the Hund’s exchange interaction. This rule dictates the energy of different configurations of electron spin, the tiny “up” or “down” magnetic moment carried by every electron. In NiPS3, this Hund’s exchange provides the energy necessary for the exciton to form.
The researchers also found that the exciton disperses through the crystal in a way that is similar to a type of spin disturbance called a “double-magnon,” another quasiparticle. Magnons, which are collective excitations of electron spins in a crystal lattice, are another facet of the intertwined electronic and magnetic behaviors in the van der Waals magnets.
“In the coming years, as instrumentation and techniques like RIXS and electron microscopy are further developed, we expect to be able to take even better measurements of NiPS3,” said postdoctoral researcher and first author of the study Wei He. “We believe that this material has outstanding potential for opening a pathway for using magnetic Hund’s excitons to realize new forms of controllable magnetic information.”
The research team also included Johnny Pelliciari and Valentina Bisogni from Brookhaven; Krzysztof Wohlfeld from the University of Warsaw in Poland; Steve Johnston from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville; Edoardo Baldini from the University of Texas at Austin; and Matteo Mitrano from Harvard University.
This study was supported by the DOE Office of Science, the University of Warsaw, the United States Army Research Office, the National Science Foundation, and Brookhaven’s Laboratory Directed Research and Development funding.
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit science.energy.gov.
Follow @BrookhavenLab on social media. Find us on Instagram, LinkedIn, X, and Facebook.
2024-21937 | INT/EXT | Newsroom