The National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II) is one of the most advanced synchrotron light sources in the world. The facility enables scientists from academia and industry to tackle the most important challenges in quantum materials, energy storage and conversion, condensed matter and materials physics, chemistry, life sciences, and more by offering extremely bright light, ranging from infrared light to x-rays.
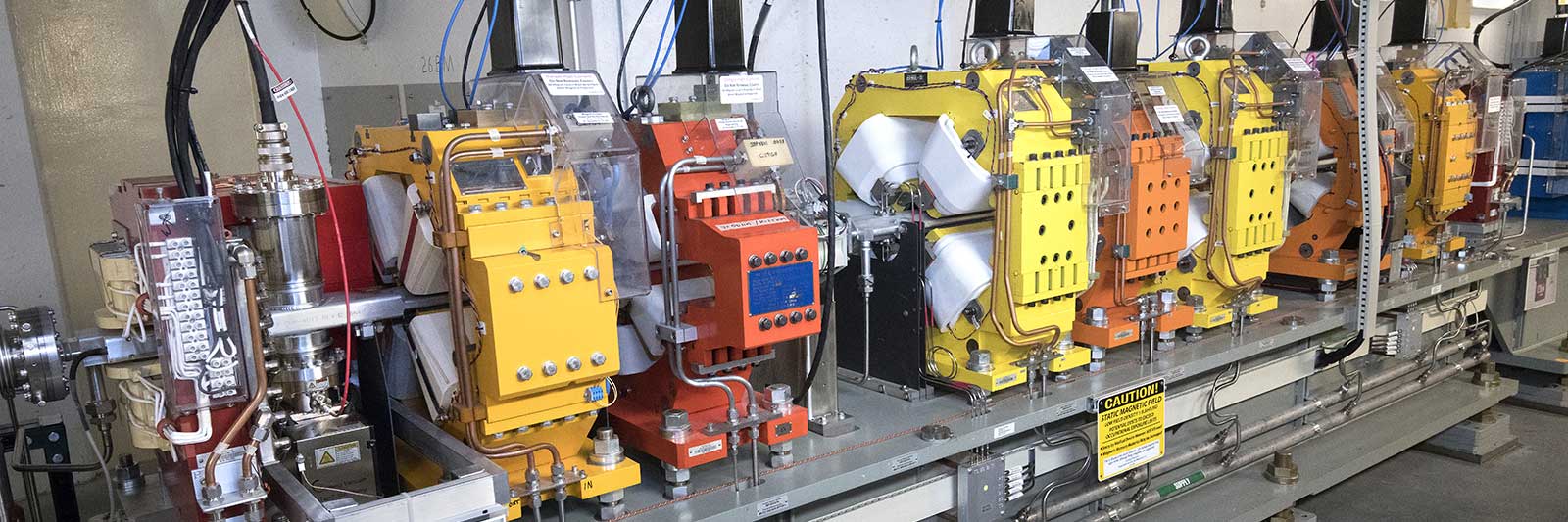
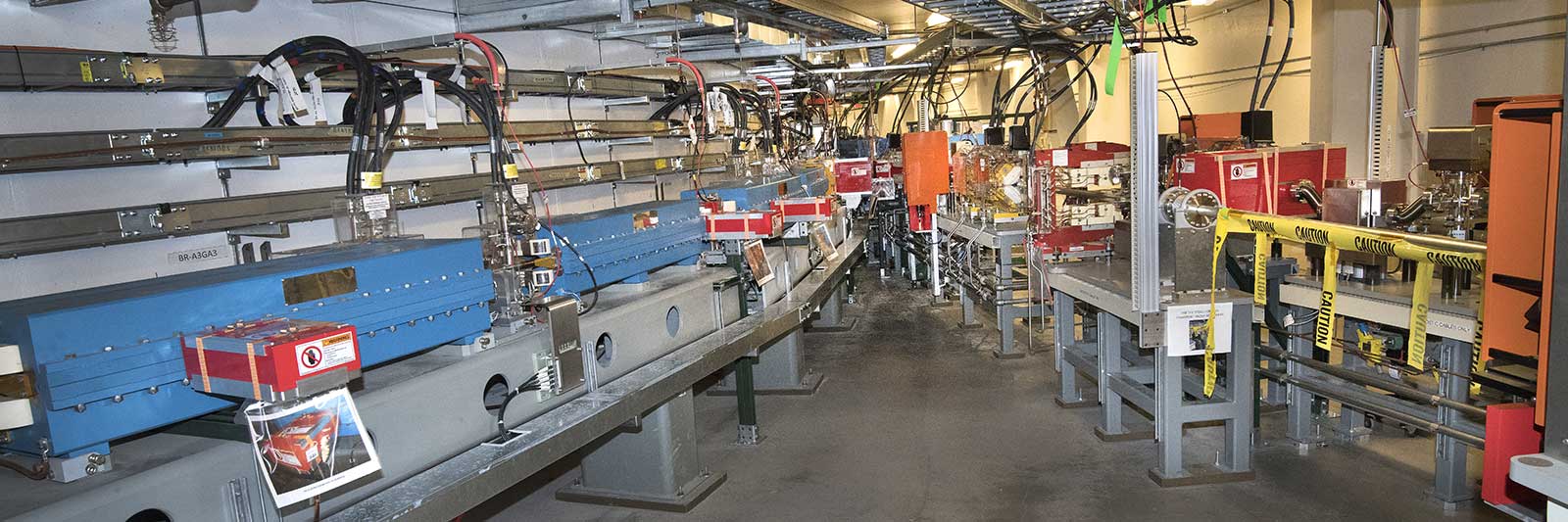
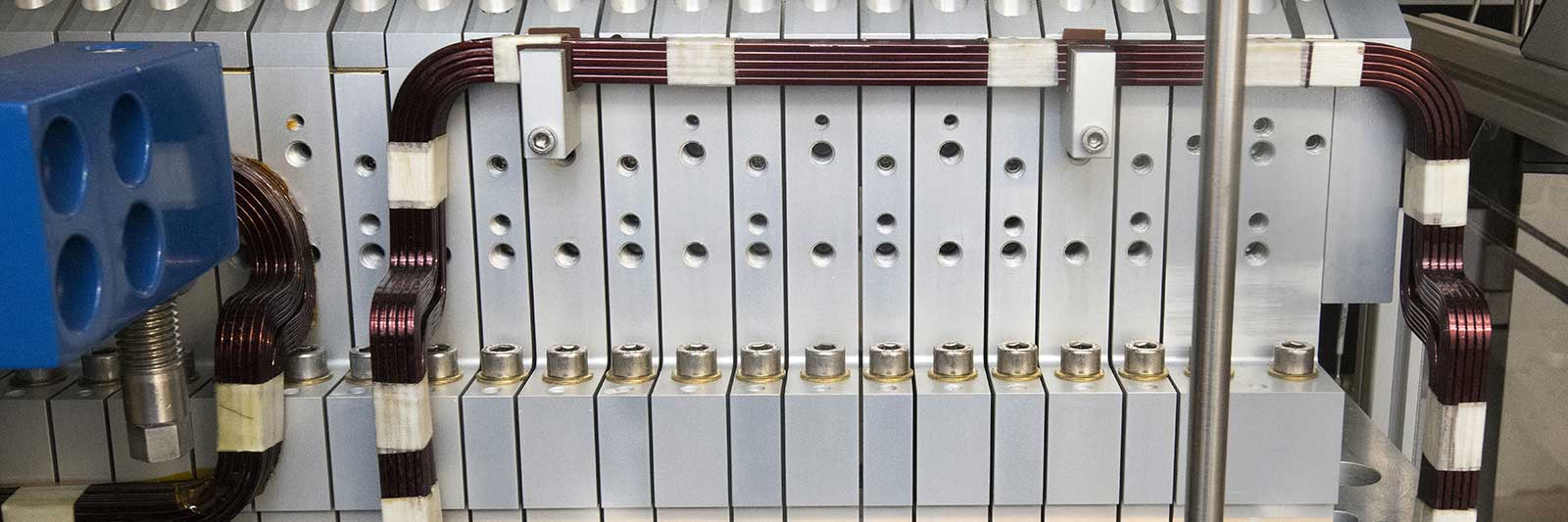
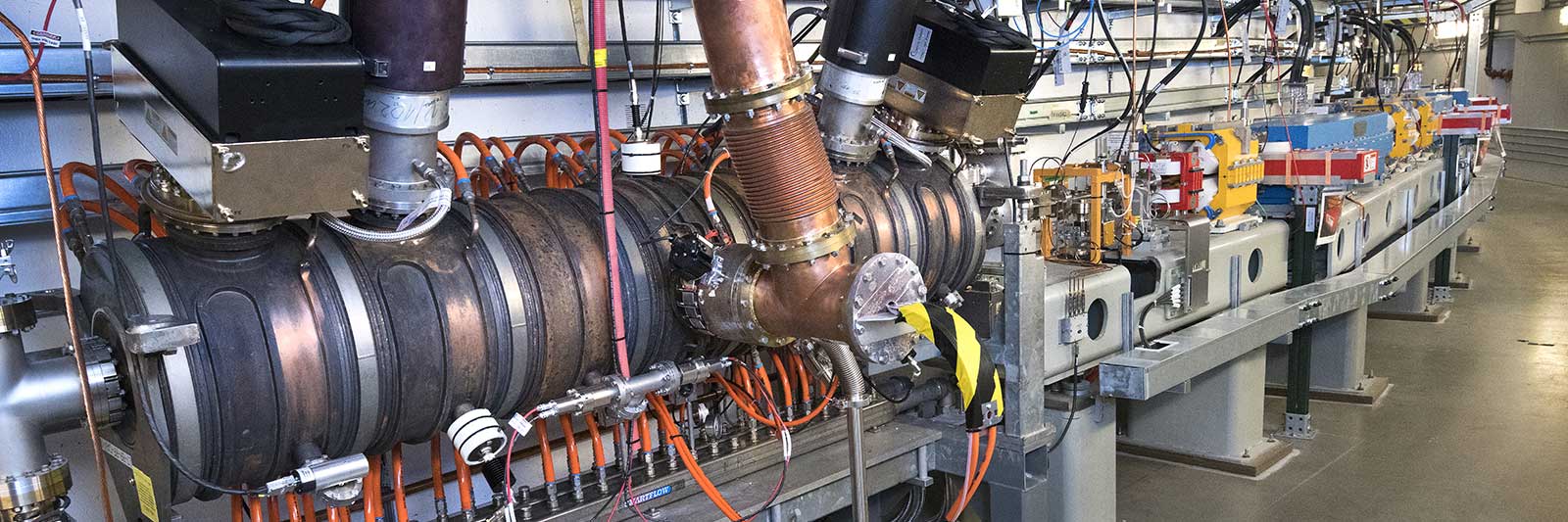
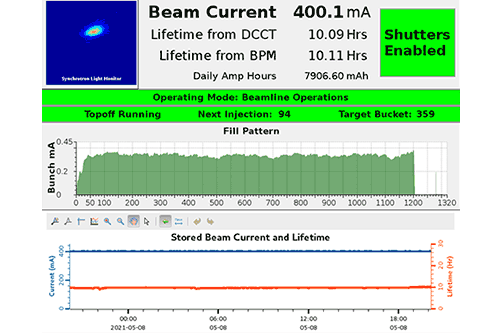
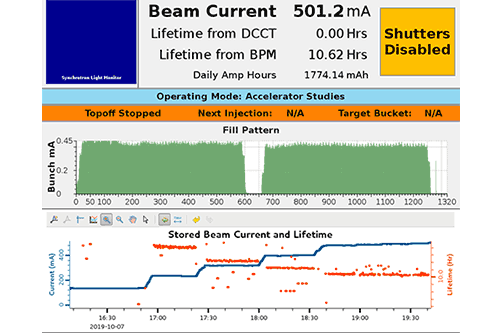
To create its intense ultrabright light, NSLS-II has an advanced particle accelerator complex that spins electrons around its half-mile-long ring at nearly the speed of light. NSLS-II’s accelerators are comprised of many complex engineering systems. Running this intense, stable electron beam for 5000 hours every year, with no interruptions, requires constant attention to every integral component.
The NSLS-II Accelerator Division focuses on securing safe and reliable machine operations while maintaining top performance. Their expertise ensures the best experimental conditions for all visiting researchers.
The Accelerator Division has built the accelerator complex, a project that lasted from 2005 to 2014. Since completion, the group operates it and continues to strive for improved performance. Furthermore, accelerator physicists and engineers from NSLS-II are planning for the future by assessing various upgrade options to increase the brightness 100-fold and enable even more exciting science in the next decade.