
NSLS-II Science Highlights
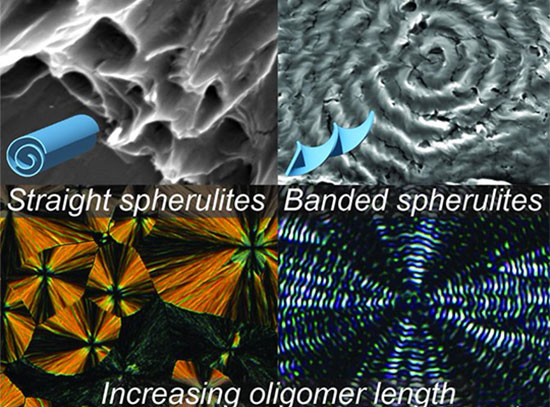
How Molecule Length Shapes Self-Assembling Materials
The length of liquid-crystal-like molecules can shape self-assembled structures without changing their core chemistry.
Observing Elusive Carriers of Angular Momentum with X-rays
Momentum- and energy-resolved observation of magnon spin current by resonant inelastic x-ray scattering captured for the first time.
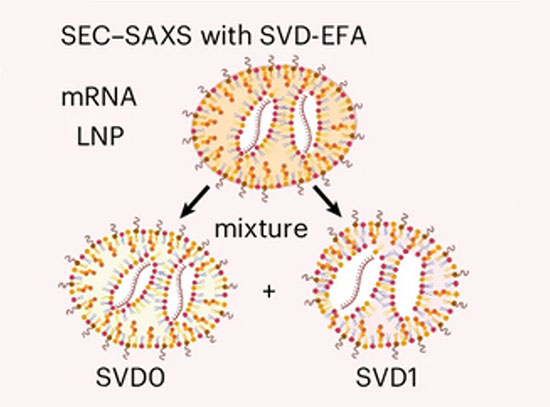
Lipid Nanoparticles: Shaping Therapeutic Delivery
Researchers discover that clinically used lipid nanoparticles have diverse, previously unrecognized shapes and internal structures.
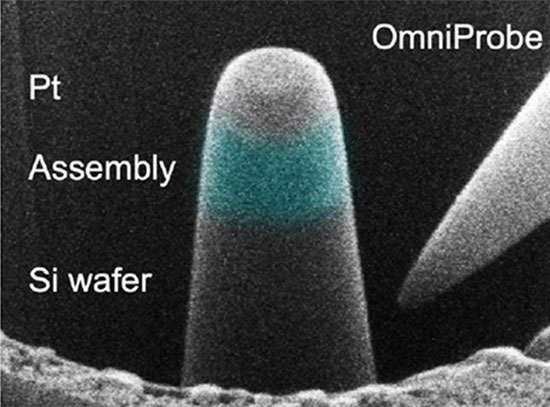
Patchy Nanoparticles by Atomic Stenciling
Scientists have developed a new way to “stencil” molecular patterns with nanometer precision.
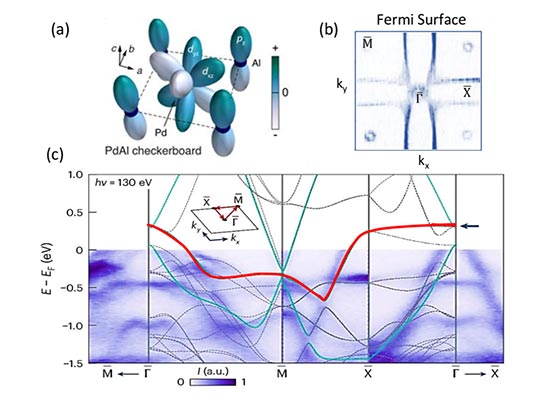
Orbital-Driven Frustrated Electron Hopping in a 2D Lattice
Scientists find a new way to achieve the exotic electronic properties of frustrated lattices in simple, stable materials.
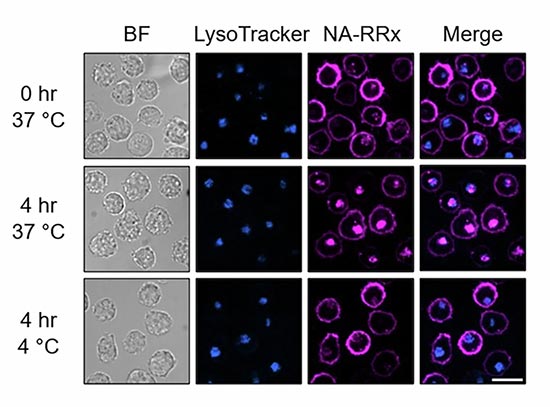
SMART Protein Splicing Enables Programmable Cell Surfaces
Researchers develop new biotechnology tool that recognizes and responds to specific sets of molecules on a cell’s surface.
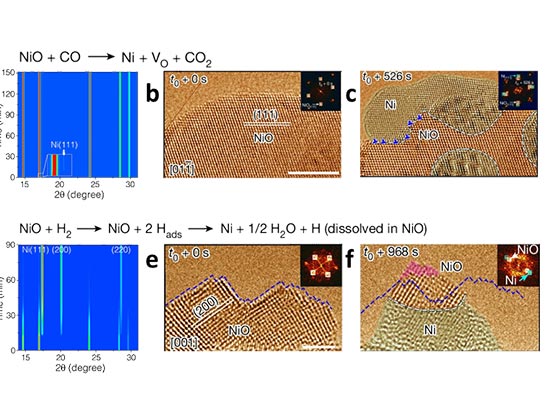
Deciphering Oxide Reduction at the Atomic Scale
Scientists reveal how CO and H2 reduce metal oxides, paving the way for improved catalysts and efficient metal production.
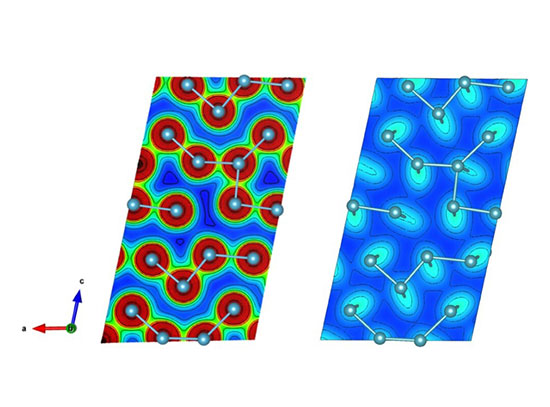
Confirmation of Covalent Bonding in α-Pu
Scientists uncover joint experimental and theoretical evidence of covalent bonding in α-plutonium for the first time
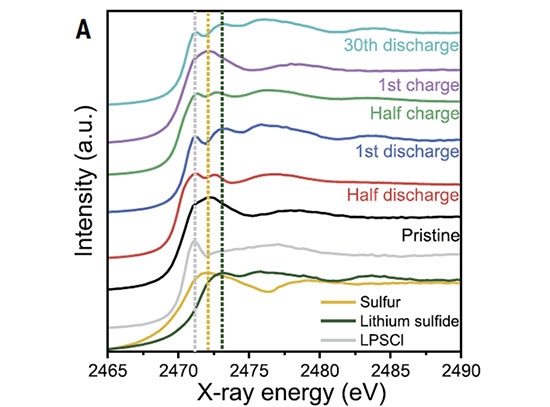
Improving Next Gen Solid-State Lithium Batteries with Halide Separation
Scientists discover technique that could lead to safer, cost-effective, longer-lasting solid-state batteries.

Improving Nitrate Removal by Woodchip Bioreactors
Scientists showed that iron and manganese can serve as reactive oxidants to enhance wood decomposition in bioreactors.
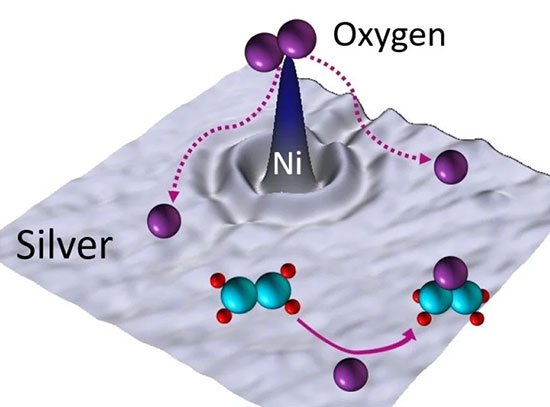
Trace Amounts of Nickel Boost Silver's Selectivity for Essential Catalysis
A research team led by Tufts University has developed a more efficient and cost-effective method for producing ethylene oxide
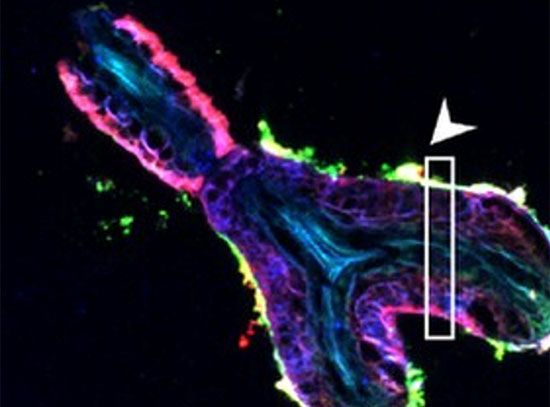
Symbiotic Fungi Liberate Iron from Soil Organic Matter and Share with Plants
Researchers discovered ectomycorrhizal fungi liberate more Fe — a limiting nutrient — from soil under specific conditions.




