Stop 6
Instrumentation Department
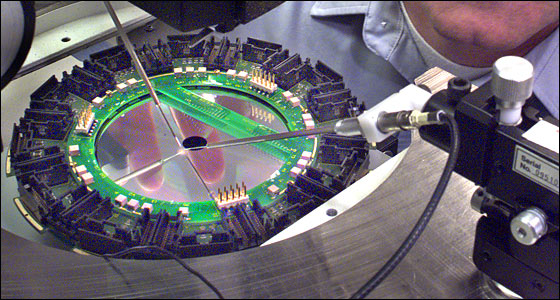
On the south side of Cornell Avenue, Brookhaven’s Instrumentation Department is pushing the frontiers of discovery by developing new technology that is not commercially available. Specialists design and fabricate state-of-the-art sensors and equipment to understand new phenomena in high-energy physics, whether it be counting just one or two electrons, creating nanostructures, or producing laser/electron pulses with the shortest ever time duration. Inventions from the division have been crucial in helping us to understand our world through research done at RHIC, the National Synchrotron Light Source, and CERN’s Large Hadron Collider.
Tandem Van de Graaff Accelerator Facility
 Across the street from Brookhaven’s Instrumentation Department, the
Tandem Van de Graaff facility provides researchers with
beams of more than 40 different types of ions, which are atoms that have been stripped of their electrons and have
many uses in scientific experiments. The Tandem consists of two 15-million-volt electrostatic accelerators each about
24-meters long. When it was completed in 1970, the Tandem was the world's largest electrostatic accelerator facility.
Across the street from Brookhaven’s Instrumentation Department, the
Tandem Van de Graaff facility provides researchers with
beams of more than 40 different types of ions, which are atoms that have been stripped of their electrons and have
many uses in scientific experiments. The Tandem consists of two 15-million-volt electrostatic accelerators each about
24-meters long. When it was completed in 1970, the Tandem was the world's largest electrostatic accelerator facility.
The Tandem has served as the ion source for RHIC and for the NASA Space Radiation Laboratory. In the spring of 2011, Brookhaven Lab commissioned its new Electron Ion Beam Source, or EBIS. While the Tandem can produce a variety of ions, EBIS is capable of making and accelerating ions of almost every element in the periodic table for these facilities. Until EBIS is ramped up to full intensity in 2012, the Tandem will provide ions for experiments and use by commercial companies and remain as a backup to EBIS while necessary.
Positron Emission Tomography Facility
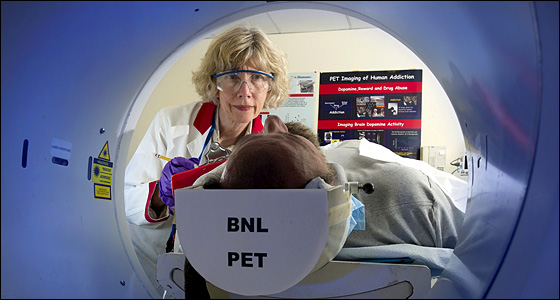 Just beyond
the Tandem Van de Graaff is the Laboratory’s facility for
Positron Emission Tomography, or PET. Brookhaven Lab has been a
pioneer in advancing medical imaging technology for more than 50 years. In the last 30 years, researchers at Brookhaven
have used PET to develop new tools for applications in human health. Major areas of medical research at the facility
include drug and alcohol addiction, and new strategies for treating obesity, eating disorders, attention deficit
hyperactivity disorder (or ADHD), and aging-related disorders.
Just beyond
the Tandem Van de Graaff is the Laboratory’s facility for
Positron Emission Tomography, or PET. Brookhaven Lab has been a
pioneer in advancing medical imaging technology for more than 50 years. In the last 30 years, researchers at Brookhaven
have used PET to develop new tools for applications in human health. Major areas of medical research at the facility
include drug and alcohol addiction, and new strategies for treating obesity, eating disorders, attention deficit
hyperactivity disorder (or ADHD), and aging-related disorders.


