Chiral Materials and Unconventional Superconductivity Group
Characterization Facilities
Magneto Optical Imaging
The Magneto Optical Imaging technique is based on Faraday effect , ie., the rotation of the light polarization induced by the magnetic field, as shown in figure 1.
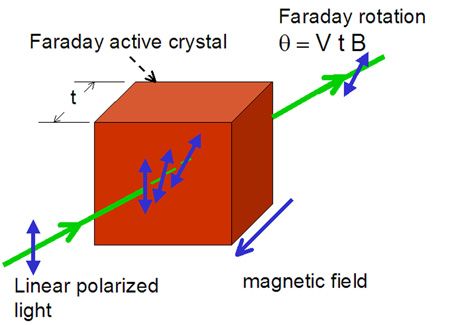
Fig. (1) Faraday effect
The Faraday effect can be used to detect the magnetic field distribution on a specimen surface by using an "indicator" film. We use a ferrimagnetic bismuth-substituted yttrium iron garnet film (Bi-YIG) with in-plane spontaneous magnetization. Application of a perpendicular magnetic field on such an indicator film will creat an out-of-plane component of the magnetization which is responsible for the Faraday rotation. If the indicator is put on a magnetic specimen, the local Faraday rotation is determined by the out-of-plane component of local magnetic field on the specimen surface, and can be detected optically. For more details about this technique, see the recent reviews:
- Magneto-optical studies of current distributions in high-Tc superconductors
Ch. Jooss, J. Albrecht, H. Kuhn, S. Leonhardt and H. Kronmueller
Rep. Prog. Phys. 65 (2002) 651-788
- Magneto-optical investigations of superconductors
M. R. Koblischka and R. J. Wijngaarden,
Supercond. Sci. Technol. 8 (1995) 199-213
- Vizualisation of magnetic flux in magnetic material and high temperature superconductors using farady effect in ferrimagnetic garnet films
Polyanskii, A. A., Cai, X. Y., Feldmann, D. M. and Larbalestier, D. C., Nano-crystalline and Thin Film Magnetic Oxides (NATO Science Series 3, High Technology 72) eds. I. Nedkov and M. Ausloos (Kluwer Academic Publishers: Netherlands) p. 353-370.
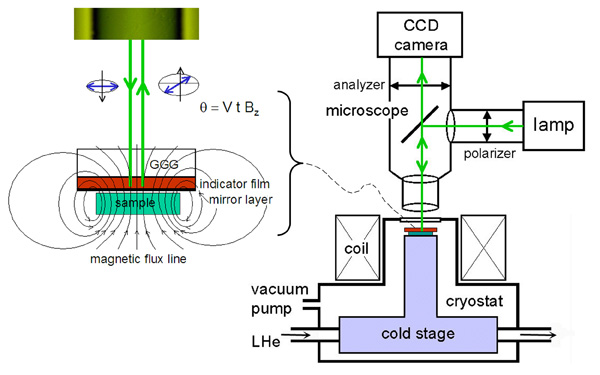
Fig. (2) The sketch of our MOI system
Fig. (3) A picture of the system
Others
- PPMS-Magneto transport and thermodynamics measurement system with 9 Tesla superconducting magnet: R-T; IV measurement; Hall effect; Specific heat, Thermal conductivity, Angular Rotator, Nernst effect; ac, dc magnetization; thermal electric power etc.
- Photolithograph, Focused Laser patterning
- SQUID magnetometer with options of ac magnetization, ultra-low field, extended dynamic range, and high temperature oven.
- AC loss




