- Home
- Facilities
- Research
-
Working at CFN
- Arrival & Departure
- Reports & Publications
- Acknowledging Use of CFN Facilities
- Data Management
- The Guide to Brookhaven
Safety Procedures
- Operations Plan
- Experimental Safety Reviews (ESR)
- COSA Training
- Hours of Operation
- Laser System Qualification
- Transport of Hazardous Materials
- Vendor On-site Scheduling Procedure (PDF)
- News & Events
- People
- Jobs
- Contact
- Business
- Intranet
Research Highlights
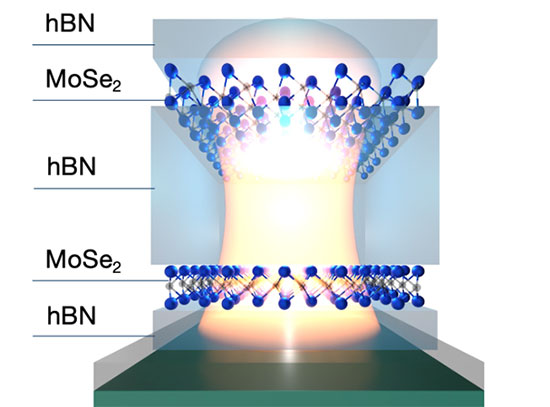
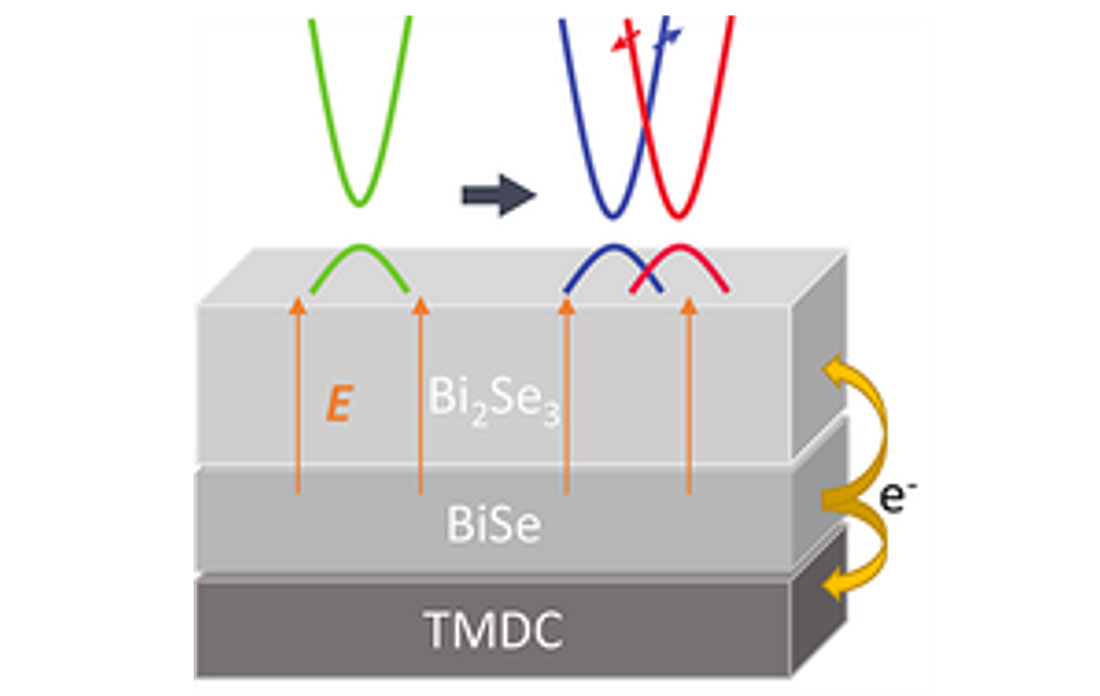
Atomically Thin Mirrors: A New Frontier in Light Confinement
This work establishes a new platform for nanoscale light manipulation using atomically thin materials, with potential use in quantum information processing, optical computing, and quantum photonics.
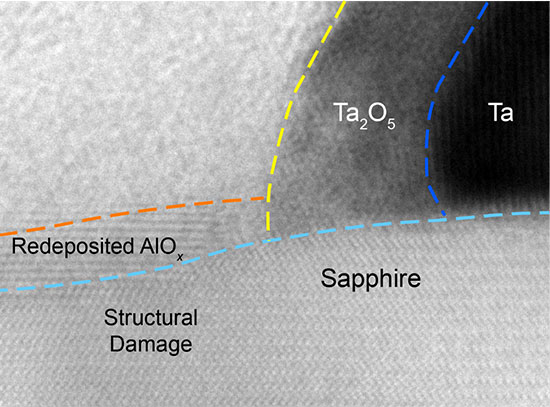
Advanced Electron Microscopy Reveals Processing Impacts on Quantum Circuits
Understanding these effects and their impact helps optimize quantum device fabrication.
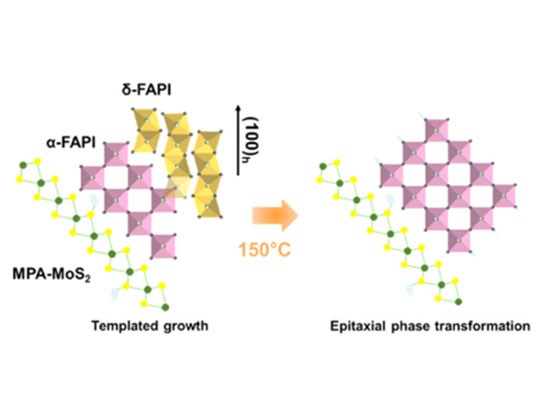
2D MoS2 Templates Unlock High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells
The work reveals a new mechanism by which 2D additives control crystallization and boost hybrid perovskite performance for solar energy conversion and optoelectronics applications.
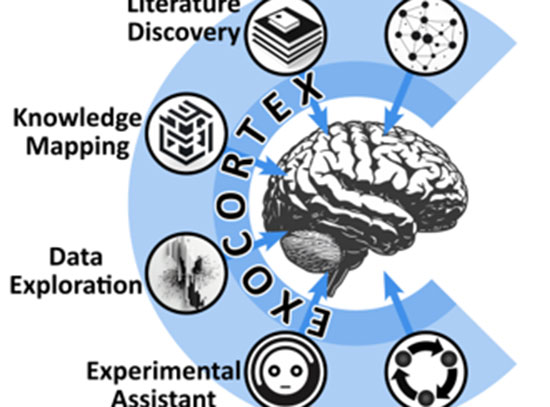
A 'Science Exocortex' Would Let Scientists Tackle Harder Problems
CFN staff are working to develop an AI-based “science exocortex” to accelerate nanomaterials discovery.
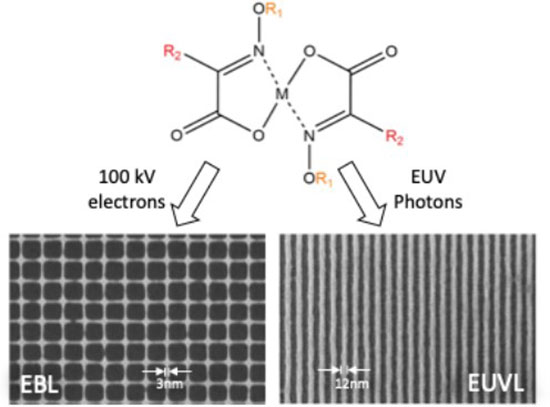
Innovative Photoresist Chemistry Brings Angstrom-Scale Patterning Within Reach
Researchers pioneered low-molecular weight photoresist platform enabling ultra high-resolution electron beam lithography (EBL) and extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) with record low roughness.
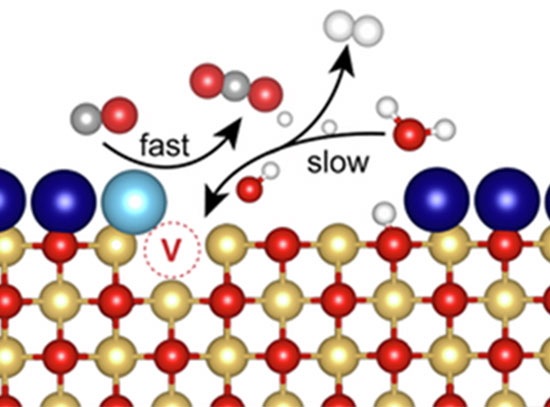
Unveiling Dynamics of Pt/CeO2 Catalysts in H2 production through the Water-Gas-Shift Reaction
CFN and NSLS-II researchers mapped the dynamic restructuring of Pt/CeO2 active sites during the water-gas-shift reaction, identifying transformation pathways critical to catalytic efficiency.
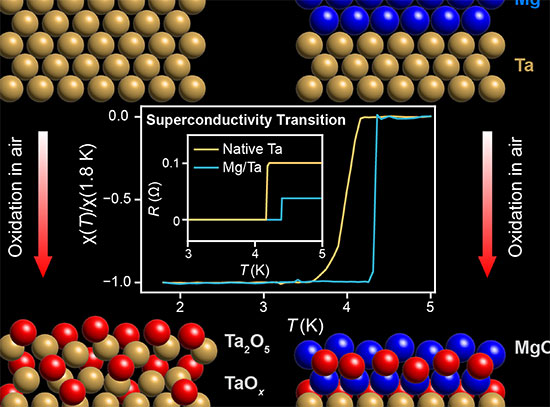
Magnesium Protects Tantalum, a Promising Material for Making Qubits
C2QA researchers and collaborators have used CFN and NSLS II facilities to demonstrate that an ultrathin magnesium (Mg) capping layer significantly suppresses the formation of tantalum (Ta) oxide, enhancing the superconducting properties of Ta thin films.
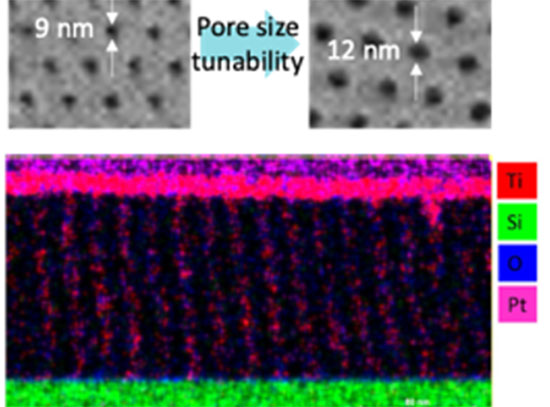
Solvent Vapor Takes Nanopore Fabrication to New Heights
CFN and Columbia researchers developed a robust protocol for fabricating highly ordered arrays of vertical nanopores in thin films using the self-assembly of a block copolymer (BCP) and solvent vapor annealing (SVA).
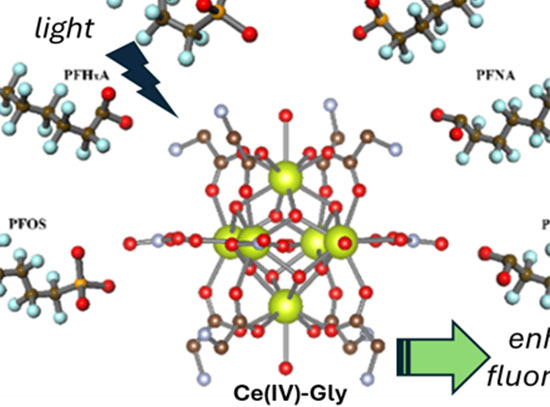
Lighting Up PFAS: Rapid Detection with Fluorescent Nanosensors
CFN users collaborated with staff to demonstrate fluorescent nanosensors using hexanuclear Cerium-oxo clusters (Ce-Gly) for rapid, one-step detection of long-chain carboxylated per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in environmental samples.
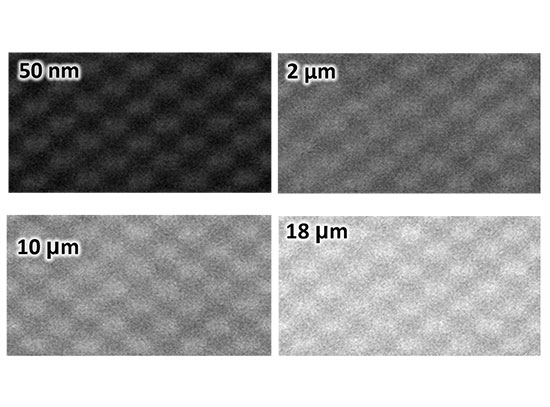
Atomic-Resolution Imaging of Bulk Samples by Scanning Electron Microscopy
Researchers demonstrated atomic-resolution secondary electron imaging in bulk crystalline samples as thick as 18 µm, using an aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope.
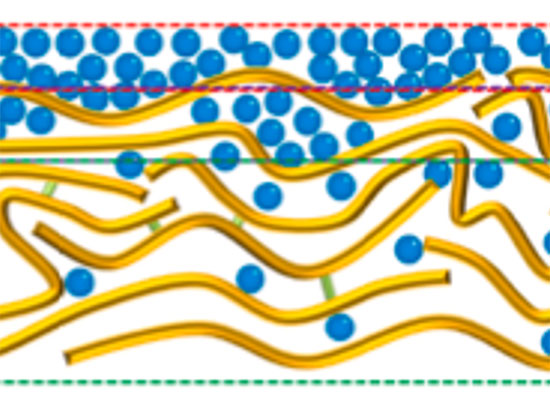
Transforming Polymer Membranes for Better Hydrogen and CO2 Separation
This work demonstrates a scalable strategy to nanoengineer polymeric membranes for improved gas separation performance, crucial for clean H2 production and carbon capture.
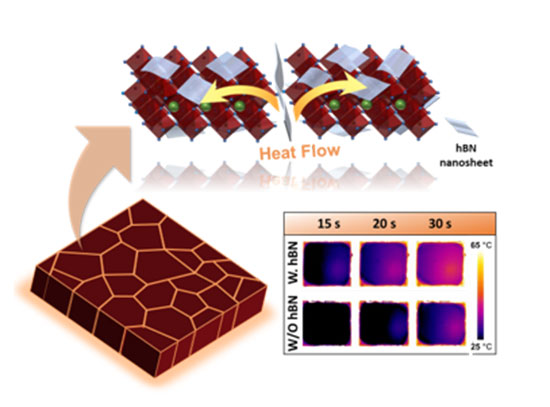
Nanosheets Increase Perovskite Solar Cell Efficiency and Stability
CFN scientists and users from Stony Brook University collaborated to discover that adding 2D hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets to perovskite solar cells expedites crystallization and grain growth, improving the cells' efficiency and stability in air.